In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficiency and adaptability are crucial for success. As third-party logistics providers (3PLs) strive to streamline their operations, many are turning to industry-specific software solutions. These tools can significantly enhance the management of logistics and value-added services processes, allowing 3PLs to provide more value to their brand customers. Below are the top five benefits of utilizing 3PL software solutions for your logistics business.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of 3PL software is its ability to improve operational efficiency. By automating various logistics processes, businesses can reduce manual errors and save time. This software often integrates with existing systems, allowing for seamless data transfer and communication. The result is a more cohesive operational framework where every department can access the same information, leading to better collaboration and fewer misunderstandings.
Streamlined Processes
3PL software solutions streamline various logistics processes, including inventory management, production planning, and order fulfillment. By centralizing these functions, 3PLs can minimize delays and enhance productivity. For instance, automated inventory updates ensure that stock levels are accurate, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts. Additionally, the software can help 3PLs forecast demand trends based on historical data, seasonal fluctuations, and market conditions. This foresight allows logistics providers to proactively adjust their inventory and staffing levels, ultimately leading to a more agile business.
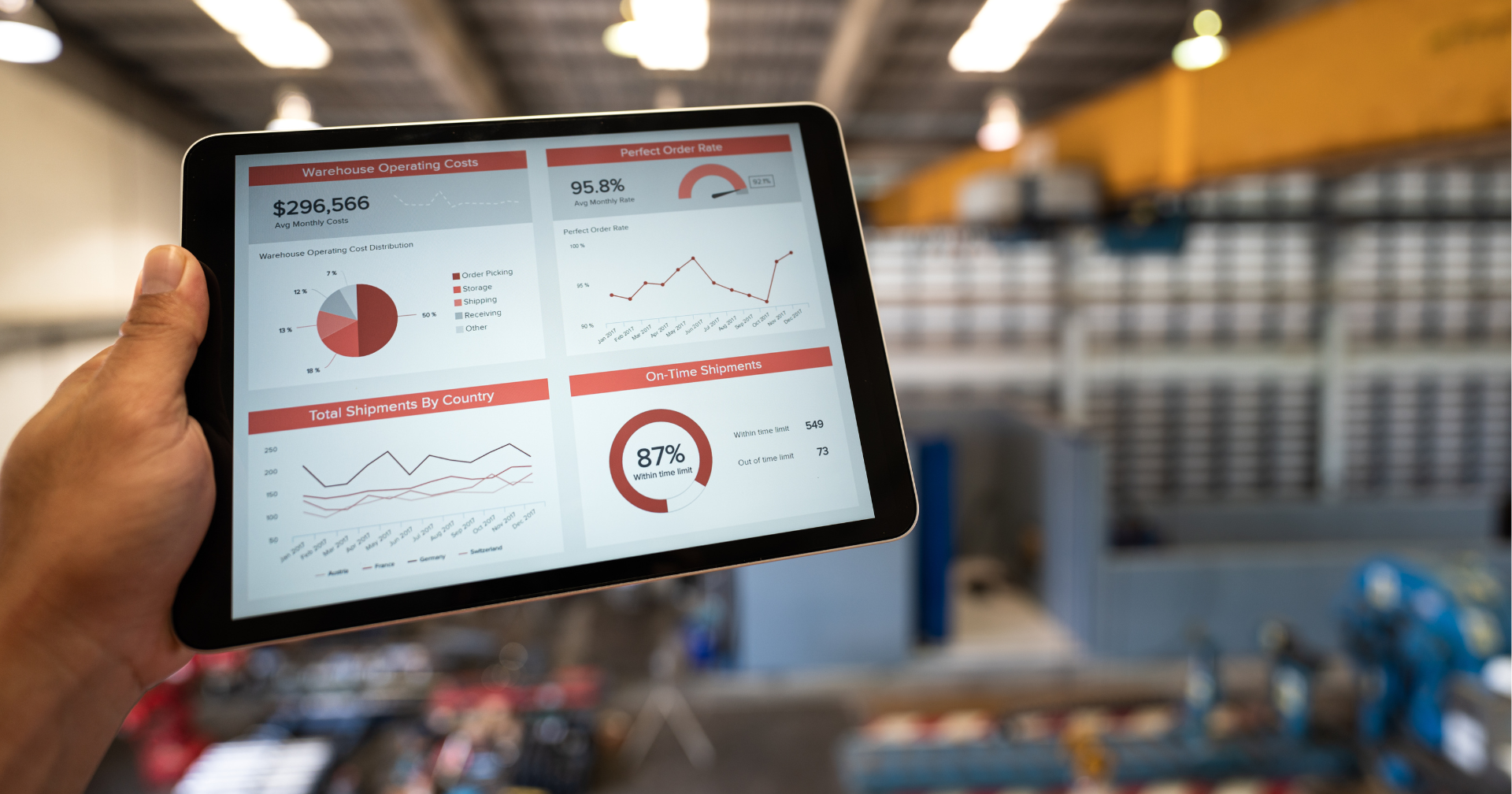
Real-Time Data Visibility
Access to real-time data is another critical feature of 3PL software. Logistics providers can monitor their production operations continuously, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly. This capability is particularly beneficial during peak seasons when demand fluctuates dramatically. With real-time insights, 3PLs can adjust their strategies on the fly, ensuring that they meet customer expectations. Furthermore, the ability to track production in real-time not only enhances transparency for the business but also improves customer satisfaction, as clients can receive timely updates about their orders. This level of visibility fosters trust and strengthens relationships between businesses and their customers, ultimately enhancing brand loyalty.
Cost Reduction Opportunities
In addition to improving efficiency, 3PL software can lead to significant cost savings. By optimizing capacity and production planning, logistics businesses can lower their overall expenditure. Moreover, the software can identify areas where waste occurs, whether it be in materials planning, production, or labor allocation. By addressing these inefficiencies, 3PLs can not only save money but also redirect those resources towards growth initiatives. This financial flexibility can be crucial for small to medium-sized logistics enterprises looking to scale their operations without incurring substantial debt.
2. Cost Reduction
Implementing 3PL software can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By optimizing logistics operations, companies can reduce overhead costs and improve their bottom line. The software helps identify inefficiencies and areas where expenses can be trimmed, allowing for more strategic resource allocation. Additionally, the integration of real-time data analytics provides businesses with insights that can further enhance cost management strategies, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Reduced Labor Costs
Automation of logistics processes also leads to reduced labor costs. With 3PL software handling tasks such as order processing and inventory management, companies can operate with fewer employees or reallocate staff to more strategic roles. This shift not only saves money but also enhances overall productivity. Moreover, by minimizing manual errors through automation, businesses can avoid costly mistakes that arise from mismanaged inventory or incorrect order fulfillment. The resulting efficiency allows companies to focus on growth initiatives rather than being bogged down by routine operational tasks, fostering a more agile and responsive business model.
Enhanced Inventory Management
Another area where 3PL software shines is in inventory management. Effective inventory control is crucial for minimizing costs associated with excess stock and stockouts. The software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling businesses to maintain optimal stock levels and reduce holding costs. By leveraging predictive analytics, companies can anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust their inventory strategies accordingly, ensuring that they are neither overstocked nor understocked. This strategic approach not only conserves capital but also enhances cash flow, allowing businesses to invest in other critical areas of their operations.
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
In today’s competitive market, customer satisfaction is paramount. 3PL software solutions can help businesses meet and exceed customer expectations through improved service delivery. By ensuring that products are delivered on time and accurately, companies can build trust and loyalty among their customer base. This trust is not only crucial for repeat business but also for generating positive word-of-mouth referrals, which can significantly impact a company’s reputation and growth potential.
Faster Order Fulfillment
Speed is a critical factor in customer satisfaction. 3PL software allows for faster order processing and fulfillment, ensuring that customers receive their products promptly. Automated workflows reduce the time it takes to fulfill, pack, and ship orders, leading to quicker turnaround times. Additionally, advanced inventory management features help businesses maintain optimal stock levels, preventing delays caused by stockouts or overstock situations. This efficiency not only satisfies customers but also optimizes operational costs, creating a win-win scenario for both the business and its clientele.
Enhanced Communication
Effective communication is essential for maintaining customer relationships. 3PL software often includes features that enhance communication between businesses and their customers. Automated notifications regarding order status and delivery updates keep customers informed and engaged throughout the purchasing process. This accessibility ensures that customers can quickly resolve any issues or inquiries, further enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction with the brand.
Data-Driven Insights
Finally, 3PL software provides valuable data-driven insights that can help businesses refine their strategies and improve customer satisfaction. By analyzing metrics such as delivery times, order accuracy, and customer feedback, companies can identify areas for improvement and implement changes that directly enhance the customer experience. This continuous feedback loop allows businesses to stay agile and responsive to customer needs, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-evolving market landscape.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow, their logistics needs evolve. 3PL software solutions offer the scalability and flexibility required to adapt to changing market conditions. Whether a company is expanding its product line or entering new markets, 3PL software can accommodate these changes seamlessly.
Adaptable to Business Growth
3PL software can easily scale with a business as it grows. Companies can add new functionalities or increase their usage without having to switch to a different system. This adaptability ensures that businesses can continue to operate efficiently, even as their logistics needs become more complex.
Support for Diverse Operations
Many businesses operate in multiple regions or offer a variety of products. 3PL software can manage diverse logistics operations from a single platform, providing a unified view of all activities. This capability simplifies management and allows for better strategic planning, regardless of the complexity of operations.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s data-driven world, the ability to make informed decisions is crucial for business success. 3PL software solutions provide valuable analytics and reporting features that help businesses analyze their logistics performance. By leveraging data, companies can identify trends, forecast demand, and make strategic decisions that drive growth.
Comprehensive Reporting Tools
3PL software typically includes comprehensive reporting tools that allow businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to logistics. These reports can provide insights into areas such as order accuracy, shipping times, and inventory turnover. By analyzing this data, companies can pinpoint inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements.
Predictive Analytics
Advanced 3PL software solutions often incorporate predictive analytics, enabling businesses to forecast future trends based on historical data. This capability allows companies to anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and make proactive decisions that enhance operational efficiency. By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Summary
Incorporating 3PL software solutions into business operations can lead to numerous benefits, from enhanced operational efficiency to improved customer satisfaction. By automating processes, reducing costs, and leveraging data for informed decision-making, companies can position themselves for long-term success. As the logistics landscape continues to evolve, investing in 3PL software is a strategic move that can help businesses thrive in a competitive environment.
As businesses navigate the complexities of logistics and supply chain management, the advantages of 3PL software become increasingly clear. With its ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, 3PL software is not just a tool; it’s a vital component of a successful business strategy. Embracing these solutions can lead to significant growth and a stronger market presence.
In conclusion, the benefits of using 3PL software solutions are manifold. Companies that adopt these technologies can expect to see improvements in efficiency, cost savings, customer satisfaction, scalability, and data-driven decision-making. As the logistics industry continues to advance, leveraging 3PL software will be essential for businesses looking to stay ahead of the competition.
Take the Next Step with Nulogy
Are you ready to unlock your business growth potential and outpace the competition? Nulogy’s specialized contract packaging and manufacturing software is the key to unlocking unparalleled production scheduling, efficiency, and accuracy in your value-added co-pack services. Don’t miss the opportunity to transform your plant operations and drive your business towards greater success.
Contact us or request a demo today to see how Nulogy can level up your value-added services in logistics.